- Home
- Services A-Z
- Endoscopy
- Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy

What Is a Colonoscopy Procedure?
A colonoscopy is a procedure to look at the inside of the colon. The colon is the large intestine and the last part of the digestive system. The colon dries, processes, and eliminates the waste left after the small intestine has absorbed the nutrients in food. The colon is about 3 to 5 feet long. It travels from the lower right corner of the abdomen (where the small intestine ends) up to the liver, across the body to the spleen in the upper left corner and then down to form the rectum and anus.
The doctor will use an instrument called the colonoscope to perform a colonoscopy. It is a long (about 5 feet), thin (about 1 inch), flexible fiberoptic camera that allows the doctor to visualize the entire colon.
A doctor may order a colonoscopy to investigate many different diseases of the colon.
Colonoscopy is best known for its use as a screening tool for the early detection of colorectal cancer.
- Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States.
- Colon cancer develops from growths within the wall of the intestine such as polyps or tumors.
- These growths often take 5 to 10 years to develop and may not cause many symptoms.
- A person may not have any symptoms of colon cancer, but having a close relative with the disease increases the risk for the disease compared to the general public.
- Most people develop polyps after age 50, so the American College of Gastroenterology (the digestive specialists) recommends screening examinations every 10 years for early detection and removal of these cancer-causing growths after that age.
Colonoscopy is also used to investigate other diseases of the colon.
- Colonoscopy may be used to find the place and cause of bleeding as well as to check areas for irritation or sores in the colon.
- These colon problems can cause unexplained changes in bowel habits.
- Pain, bloody diarrhea, and weight loss can be caused by inflammation of the bowel, which may be the result of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
- These inflammatory digestive diseases tend to occur in young adults and, if undetected, can produce chronic symptoms and increase the risk of colon cancer.
Colonoscopy is used when there is concern a disease of the colon may exist.
- The doctor may recommend this test if other screening tests such as a manual rectal examination, a fecal occult blood test (a test that detects blood in the feces), or a barium enema (a test in which barium is used to make the colon visible on an X-ray) suggest that further information is needed to make a diagnosis.
- A colonoscopy may be required when symptoms of digestive disease or other warning signs are present.
- Rectal bleeding (which may appear as bright red, very dark, or black)
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Changes in bowel habits
- Non-dietary weight loss
- A new test called Cologuard, a stool-based colorectal screening test that detects the presence of red blood cells and DNA mutations, may indicate the presence of certain kinds of abnormal growths that may be cancers such as colon cancer or precursors to cancer. If this test reveals the possibility of colon cancer, a colonoscopy may be necessary.
Only doctors who specialize in the study of digestive or rectal diseases, have special training in endoscopy, and are certified to perform colonoscopy qualify to perform this procedure.
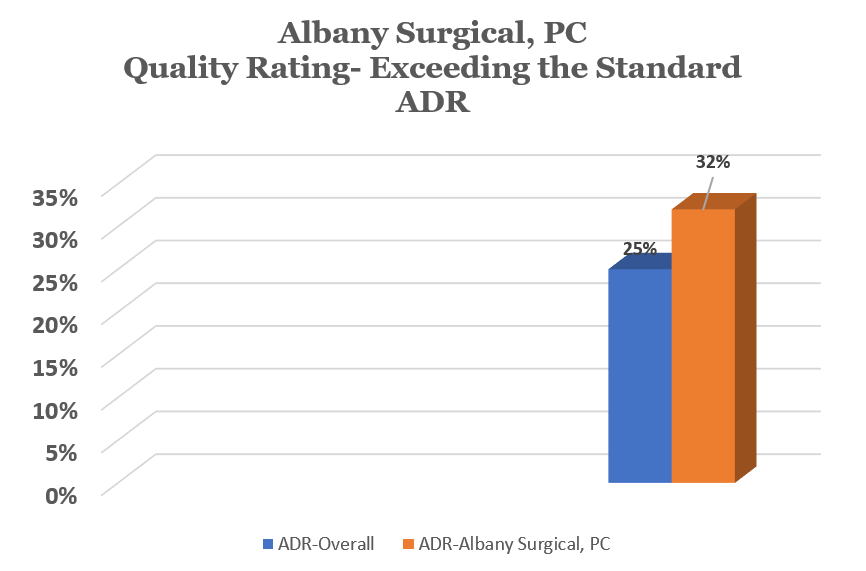
ADR
The Adenoma Detection Rate (ADR) is the most important quality measure for screening colonoscopies. The ACG/American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) recommends an overall ADR rate for screening colonoscopies in the US of 25% for all patients. The ADR is calculated as a percentage of first-time screenings in patients at 50 years of age at which a precancerous polyp (adenoma) is discovered.
In short, if a physician performs 10 screening colonoscopies and finds an adenoma in two (2) patients, the ADR is 20%, which is 5% lower than the recommended national ADR. At Albany Surgical, P.C., our overall ADR is 32%, which is 7% higher than the recommended ADR.